Volume 115, Nº 2, August 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20190368
REVIEW ARTICLE
Serum Levels of BDNF in Cardiovascular Protection and in Response to Exercise
Ivani Credidio Trombetta
José Roberto DeMoura
Cleber Rene Alves
Renato Carbonari-Brito
Felipe Xerez Cepeda
José Ribeiro Lemos Jr.
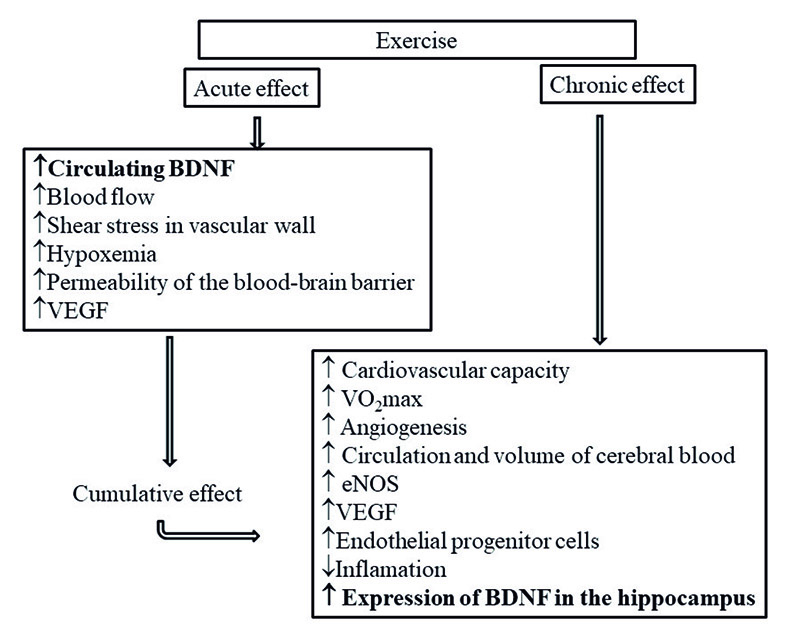
Figure 1 – Acute and chronic effect of physical exercise on cardiovascular aspects related to BDNF (Adapted from Stimpson et al, 2018).
Abstract
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is currently the leading cause of death in Brazil and worldwide. In 2016, CVD accounted for more than 17 million deaths, representing 31% of all deaths globally. Molecular and genetic mechanisms may be involved in vascular protection and should be considered in new therapeutic approaches. In this sense, recent studies have reported that brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is reduced in individuals predisposed to develop CVD, and that aerobic physical training increases the amounts of circulating BDNF. BDNF is a neurotrophin found at high concentrations in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex and is considered a key molecule for the maintenance of synaptic plasticity and survival of neuronal cells. In addition to neuronal plasticity, BDNF is also important in vascular function, promoting angiogenesis through the regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). However, a variant of the BDNF gene in humans, the Val66Met polymorphism (substitution of the amino acid valine for a methionine at position 66 of the codon), occurring in 20-30% of the Caucasian population, may affect plasma BDNF concentrations and its activity in all peripheral tissues containing tyrosine kinase B receptors (TrkB), such as the endothelium. Thus, we will present a discussion about the role of serum BDNF levels in cardiovascular protection, Val66Met genetic variant in vascular reactivity and the effect of physical exercise.
Keywords: Cardiovascular Diseases/mortality; BDNF; Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor; Endothelium Vascular; Nerve Growth Factors; Neuronal Plasticity; Polymorphism; Exercise.















