Volume 114, Nº 3, March 2020
https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20180386
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Nome do Artigo
Márcio Augusto Silva
Guilherme Muller de Campos Futuro
Erick Sessa Merçon
Deborah Vasconcelos
Rovana Silva Agrizzi
Jorge Elias Neto
Ricardo Kuniyoshi
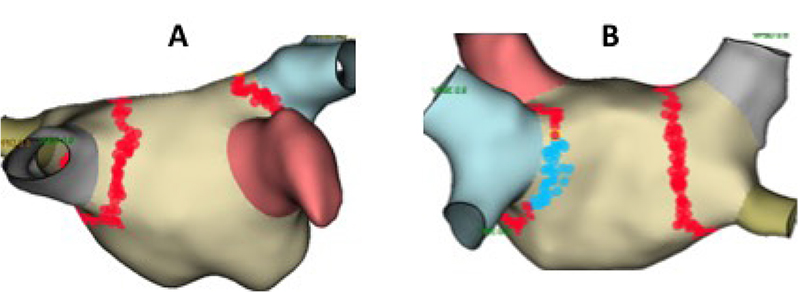
Figure 2 – Radio Frequency Applications. Images generated by left atrial geometric reconstruction using an electroanatomical mapping system (Ensite/NAVX – St. Jude Medical/Abbott). A – Previous view. Dots in red show the radiofrequency applications. B – Posterior view. Blue dots show locations of radiofrequency applications where esophageal temperature increases.
Abstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation under uninterrupted warfarin use is safe and recommended by experts. However, there is some controversy regarding direct-acting oral anticoagulants for the same purpose.
Objective: To evaluate the safety of AF ablation under uninterrupted anticoagulation with rivaroxaban.
Methods: A series of 130 patients underwent AF radiofrequency ablation under uninterrupted rivaroxaban use (RIV group) and was compared to a control group of 110 patients under uninterrupted warfarin use (WFR group) and therapeutic International Normalized Ratio (INR). We analyzed death, rates of thromboembolic events, major and minor bleedings, activated clotting dose in the procedure. The ablation protocol basically consisted of circumferential isolation of the pulmonary veins guided by electroanatomic mapping. It was adopted a statistical significance of 5%.
Results: The clinical characteristics of the groups were similar, and the paroxysmal AF was the most frequent type (63% and 59%, RIV and WFR groups). A thromboembolic event occurred in the RIV group. There were 3 patients with major bleeding (RIV = 1 and WFR = 2; p = 0.5); no deaths. Basal INR was higher in the WFR group (2.5 vs. 1.2 ± 0.02; p < 0.0001), with similar basal ACT levels (123.7 ± 3 vs. 118 ± 4; p= 0, 34). A higher dose of venous heparin was used in the RIV group (9,414 ± 199 vs. 6,019 ± 185 IU; p < 0.0001) to maintain similar mean ACT levels during the procedure (350 ± 3 vs. 348.9 ± 4; p = 0.79).
Conclusion: In the study population, AF ablation under uninterrupted rivaroxaban showed a safety profile that was equivalent to uninterrupted warfarin use with therapeutic INR. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020; 114(3):435-442)
Keywords: Catheter Ablation/methods; Atrial Fibrillation; Rivaroxaban /therapeitic use; Anticoagulants/therapeutic use; Anticoagulants/adverse effects.















