Volume 114, Nº 3, March 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20190036
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Creation and Implementation of a Prospective and Multicentric Database of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: RIAM
Jacqueline Vaz
Anibal Pereira Abelin
Marcia Moura Schmidt
Pedro Piccaro de Oliveira
Carlos A. M. Gottschall
Clarissa Garcia Rodrigues
Alexandre Schaan de Quadros
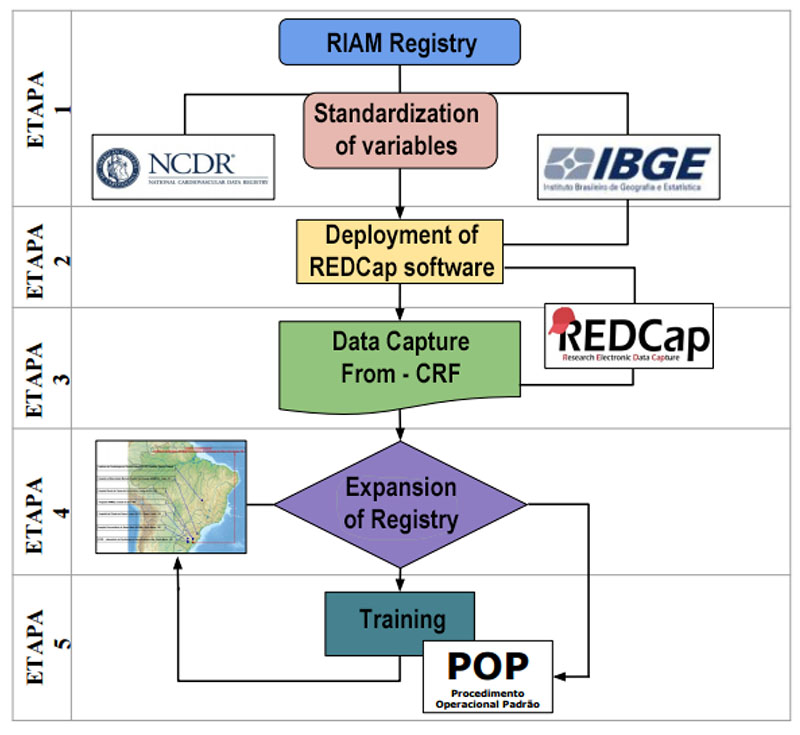
Figure 1 – Improvement and expansion flowchart for the multicenter Registry of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Source: Lucidchart. Available in: https://www.lucidchart.com
Abstract
Background: Multicenter registries representing the real world can be a significant source of information, but few studies exist describing the methodology to implement these tools.
Objective: To describe the process of implementing a database of ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction (STEMI) at a reference hospital, and the application of this process to other centers by means of an online platform.
Methods: In 2009, our institution implemented an Registry of Acute Myocardial Infarction (RIAM), with the prospective and consecutive inclusion of every patient admitted to the institution who received a diagnosis of STEMI. From March 2014 to April 2016, the registries were uploaded to a web-based system using the REDCap software and the registry was expanded to other centers. Upon subscription, the REDCap platform is a noncommercial software made available by Vanderbilt University to institutions interested in research.
Results: The following steps were taken to improve and expand the registry: 1. Standardization of variables; 2. Implementation of institutional REDCap (Research Electronic Data Capture); 3. Development of data collection forms (Case Report Form - CRF); 4. Expansion of registry to other reference centers using the REDCap software; 5. Training of teams and participating centers following an SOP (Standard Operating Procedure). Conclusion: The description of the methodology used to implement and expand the RIAM may help other centers and researchers to conduct similar studies, share information between institutions, develop new health technologies, and assist public policies regarding cardiovascular diseases. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020; 114(3):446-455)
Keywords: Myocardial Ischemia/physiopathology; Cardiovascular Diseases/mortality; Myocardial Infarction/ physiopathology; Multicenter Study; Database; Public Health Policy.















