Volume 114, Nº 1, January 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20180258
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Left Ventricular Remodeling Patterns in Primary Healthcare
Roberto de Castro Meirelles de Almeida
Antonio José Lagoeiro Jorge
Maria Luiza Garcia Rosa
Adson Renato Leite
Dayse Mary S. Correia
Evandro Tinoco Mesquita
Sergio Chermont
Jocemir Ronaldo Lugon
Wolney de Andrade Martins
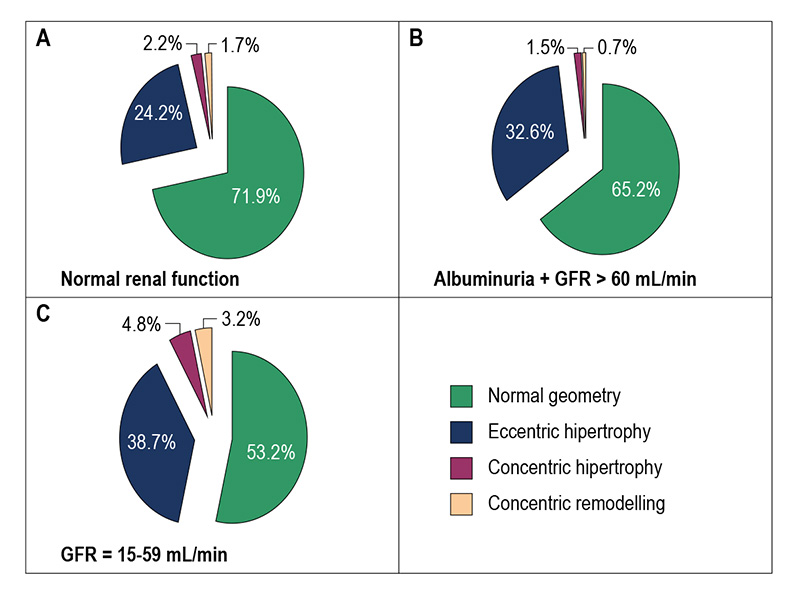
Figure 1 – A, B, and C: Evaluation of parameters of renal function in different patterns of left ventricular remodeling.
Abstract
Background: Left ventricular remodeling (LVR) is related to both non-fatal and fatal outcomes.
Objective: To describe the geometric patterns of the LV and their associations.
Methods: A total of 636 individuals between the ages of 45 and 99 years in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, were submitted to clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, electrocardiogram, and tissue Doppler echocardiography (TDE). The difference between categories was tested with Kruskall-Wallis with post hoc tests, once all variables studied are non-normally distributed and Pearson’s Qui-square (categorical variables). Gross and adjusted ORs were estimated by logistic regression. The level of significance was 5% for all tests. Subjects had LVR characterized as: normal geometry (NG), concentric remodeling (CR), concentric hypertrophy (CH), and eccentric hypertrophy (EH).
Results: The prevalence of altered patterns was 33%. Subjects presented NG (n = 423; 67%); EH (n = 186; 29%); CH (n = 14; 2%); and CR (n = 13; 2%). The variables of gender, age, level of education and albumin/creatinine ratio (A/C), showed a relationship with the chance of EH even after adjustment.
Conclusion: Approximately one third of the studied individuals had LVR and were at risk for developing heart failure. Altered A/C in urine was associated with EH, indicating an early relationship between cardiac and renal dysfunction. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020; 114(1):59-65)
Keywords: Cardiovascular Diseases/physiopathology; Ventricular Remodeling; Hypertrophy, Left Ventricular; Heart failure; Renal Insufficiency; Risk Factors/complications; Comorbidity.















