Volume 111, Nº 2, August 2018
DOI: http://www.dx.doi.org/10.5935/abc.20180108
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Pioglitazone Induces Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Inhibits Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy Via VEGFR-2 Signaling Pathway
Wenliang Zhong
Wen Jin
Shanghua Xu
Yanqing Wu
Shunxiang Luo
Minlie Liang
Lianglong Chen
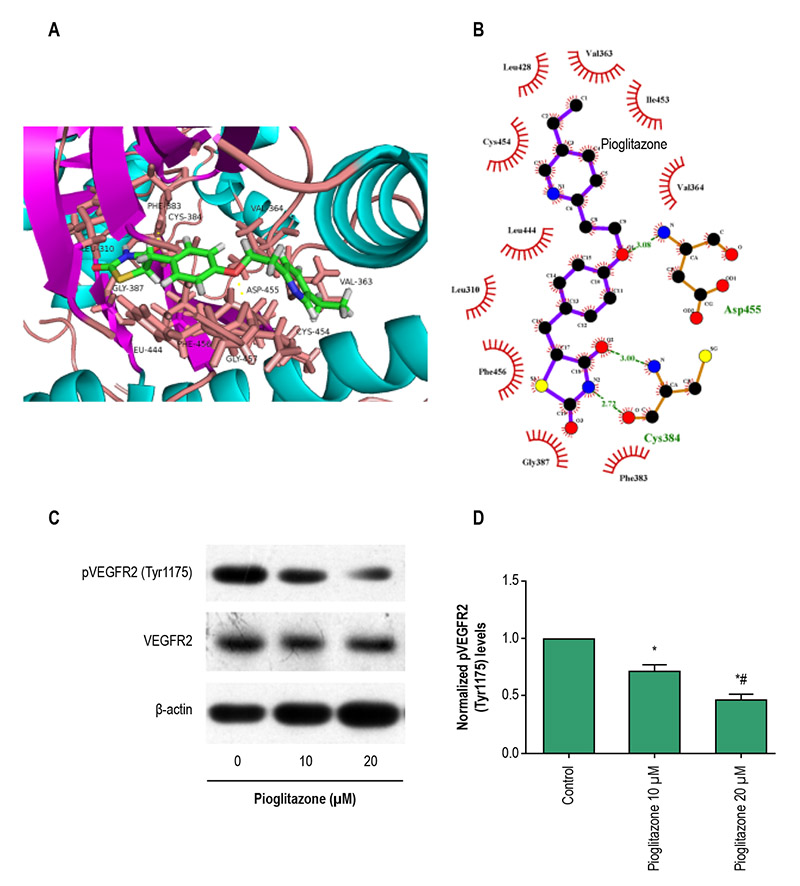
Figure 1 – VEGFR-2 is the potential target of pioglitazone. A, 3D molecular docking model of pioglitazone with VEGFR-2; green structure, the conformer of pioglitazone. B, 2D molecular docking model of pioglitazone with VEGFR-2; purple structure, the conformer of pioglitazone. H-bonding interactions between the pioglitazone and VEGFR-2 were indicated with green dashed lines. C and D, Representative western bolotting trace of VEGFR-2 and phospho-VEGFR-2 (Tyr1175) protein levels in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes under hypertrophic stimuli, and treated with 0, 10, 20 (μM) pioglitazone for 24 hours, and intensity of the bands in C normalized to β-actin (n = 12 in each group). All data shown are the mean ± SD. *p < 0.01 compared with control; #p < 0.01 compared with pioglitazone 10 μM group, calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Bonferroni test for pairwise comparisons.
Abstract
Background: Pioglitazone has been widely used as an insulin-sensitizing agent for improving glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, cardiovascular risk and protective effects of pioglitazone remain controversial. Objectives: In this study, we investigated whether pioglitazone affects cardiomyocyte apoptosis and hypertrophy by regulating the VEGFR-2 signaling pathway.
Methods: Cardiomyocytes were enzymatically isolated from 1- to 3-day-old Sprague-Dawley rat ventricles. Effects of pioglitazone and the VEGFR-2-selective inhibitor apatinib on cardiomyocyte apoptotic rate was determined using flow cytometry, and hypertrophy was evaluated using [3H]-leucine incorporation. The protein expressions of unphosphorylated and phosphorylated VEGFR-2, Akt, P53, and mTOR were determined by Western-Blotting. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to assess the differences between groups.
Results: Pioglitazone and VEGFR-2-selective inhibitor apatinib reduced rat cardiomyocyte viability and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II in vitro. Furthermore, in the same in vitro model, pioglitazone and apatinib significantly increased the expression of Bax and phosphorylated P53 and decreased the expression of phosphorylated VEGFR-2, Akt, and mTOR, which promote cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.
Conclusions: These findings indicate that pioglitazone induces cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inhibits cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by modulating the VEGFR-2 signaling pathway. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018; 111(2):162-169)
Keywords: Apoptosis; Myocytes, Cardiac; Cardiomegaly; Heart Failure/physiopathology; Antihypertensive Agents; Thiazolidinediones; Insulin Resistance















