Volume 115, Nº 2, August 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20190780
VIEWPOINT
Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension: From the Golden Trio to the Octet
Audes Diógenes Magalhães Feitosa
Marco Mota-Gomes
Oswaldo Passarelli Júnior
Weimar Kunz Sebba Barroso
Roberto Dischinger Miranda
Eduardo Costa Duarte Barbosa
Andrea A. Brandão
Wilson Nadruz
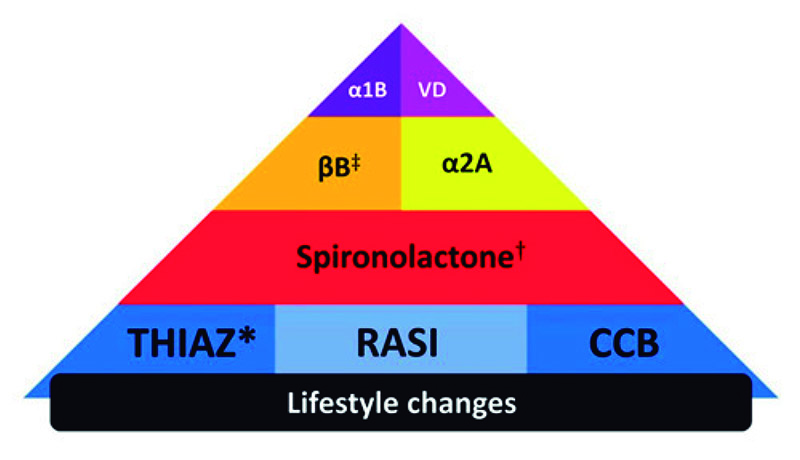
Figure 1 – Structured octet for the treatment of hypertension. THIAZ: thiazide-type/thiazide-like diuretic; RASI: renin angiotensin system inhibitor; CCB: calcium-channel blocker; βB: Beta-blocker; α2A: central alpha-2 agonist; α1B: alpha-1 adrenergic blocker; VD: direct vasodilator. *When BP control is not achieved with THIAZ, RASI and CCB, and the THIAZ is hydrochlorothiazide, substitute this latter drug by a long-acting THIAZ (chlortalidone or indapamide). If glomerular filtration rate <30 mL/min, substitute THIAZ by a loop diuretic, such as furosemide. †If spironolactone is not tolerated, particularly due to anti-androgenic side effects, consider substituting this drug by amiloride. ‡βB is indicated as the first choice for the initial treatment when there are specific indications, such as angina, post-myocardial infarction, heart failure, arrhythmia or heart rate control.
Keywords: Hypertension; Antihypertensive Agents; Drug Therapy; Life Style; Exercise; Weight Loss; Medication Adherence.















