Volume 115, Nº 1, July 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20200427
CASE REPORT
SARS-Cov-2 Infection and Pulmonary Thromboembolism – The Prothrombotic State in COVID-19
Hellen Dutra Passos
Mariana Carvalho Alves
Leonardo Baumworcel
João Paulo Cerqueira Vieira
Juliane Dantas Seabra Garcez
Antônio Carlos Sobral Sousa
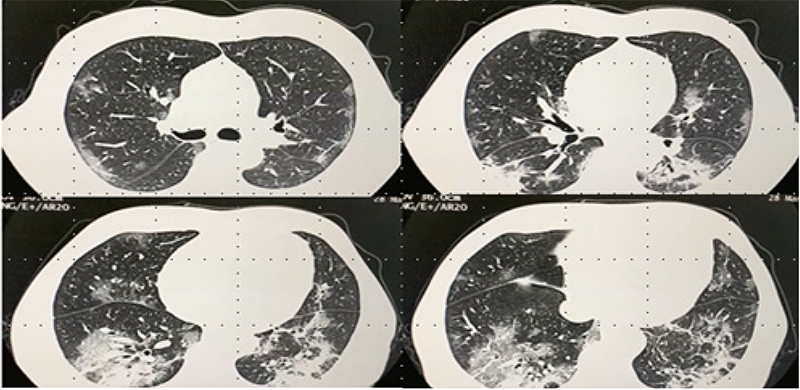
Figure 1 – Chest computed tomography without contrast on hospital admission. Ground-glass opacities, mainly in peripheral areas and more evidently in lower segments,affecting less than 50% of the pulmonary parenchyma.
Keywords: Coronavirus; COVID-19; Pulmonary Embolism; Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome; Anticoagulants; Diagnostic, Imaging.















