Volume 114, Nº 4, April 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20190055
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Hydrotherapy Reduces Arterial Stiffness in Pregnant Women with Chronic Hypertension
Giovana Macêdo Linhares
Antonio Vieira Machado
Marcus Vinícius Bolívar Malachias
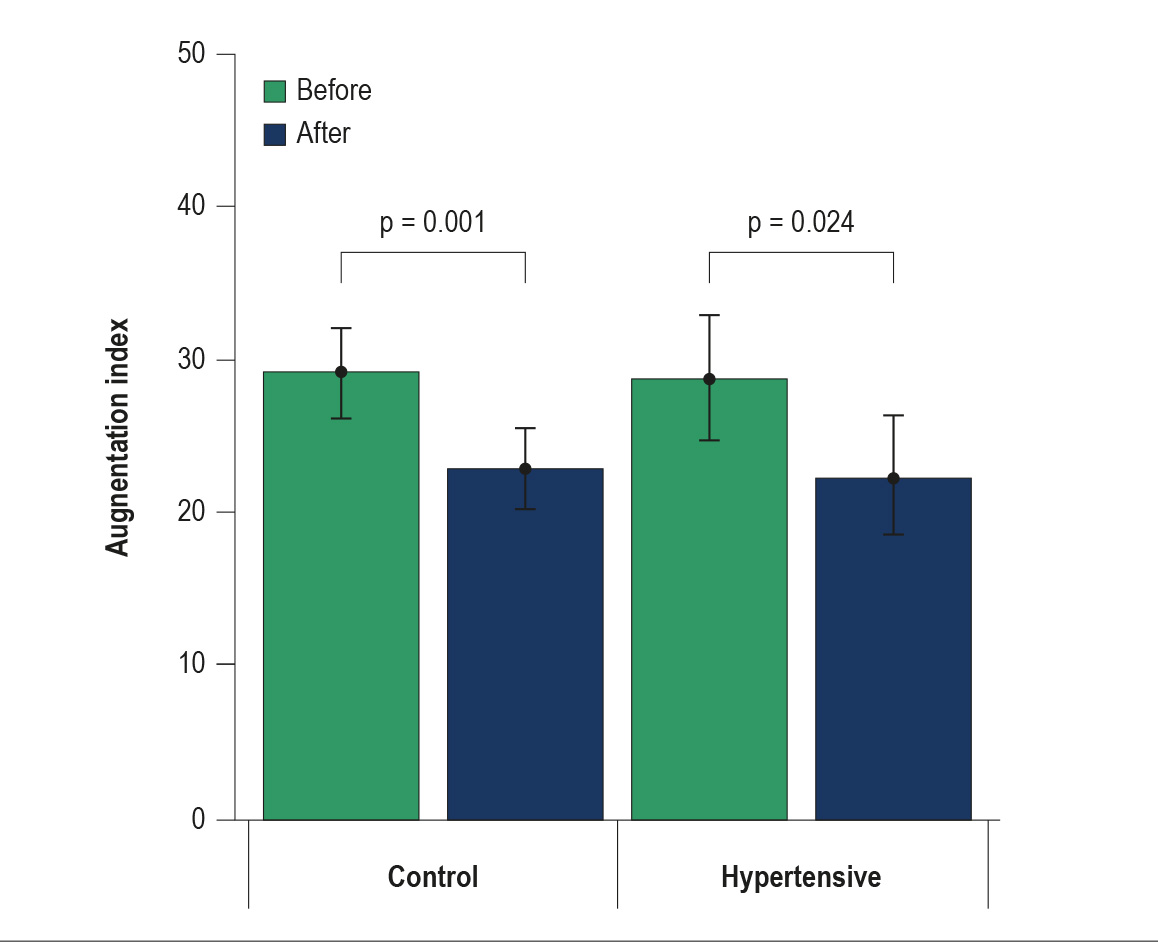
Figure 1 – Reduction in the augmentation index adjusted for a heart rate of 75 bpm (Alx@75) (%) before and after a hydrotherapy session in the control (CG) and hypertensive (HG) groups.
Abstract
Background: Chronic hypertension (CH) and high arterial stiffness (AS) increase the risk of complications during pregnancy, such as superimposed preeclampsia and low fetal growth.
Objective: To evaluate the impact of hydrotherapy, a non-pharmacological treatment strategy, on AS in pregnant women with CH.
Methods: Cross-sectional study evaluating the effect of a standardized hydrotherapy session on AS in pregnant women with CH and controls. We used the device Mobil-O-Graph® NG to measure blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), and AS before and after a hydrotherapy session involving stretching, warming up, strengthening, and relaxation. The level of significance adopted in the statistical analyses was 5%.
Results: We evaluated 36 pregnant women, including 12 with hypertension (HG) and 24 controls (CG), aged 30.4 ± 4.8 years and at 29.2 ± 3.3 gestational weeks. Hydrotherapy promoted in both groups a significant reduction in AS assessed by the augmentation index at a HR of 75 bpm (AIx@75) (HG: 28.8 ± 7.3%, before; 22.4 ± 6.9%, after; p = 0.024; and CG: 29.1 ± 7.4%, before; 22.9 ± 6.6%, after; p = 0.001), as well as a reduction in HR (HG: 93.4 ± 11.8 bpm, before; 82.4 ± 10.0 bpm, after; p < 0.001; and CG: 91.4 ± 13.4 bpm, before; 81.5 ± 12.6 bpm, after; p < 0.001), but a nonsignificant reduction in BP.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that a hydrotherapy session acutely reduces AS assessed by AIx@75, and may represent a potential non‑pharmacological strategy to prevent maternal and fetal complications in pregnant women with CH. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020; 114(4):647-654)
Keywords: Hypertension; Hydrotherapy; Pregnancy, High-Risk Ris/complications; Vascular Stiffness; Pre-Eclampsia.















