Volume 113, Nº 6, December 2019
DOI: http://www.dx.doi.org/10.5935/abc.20190226
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The Usefulness of Admission Plasma NT-pro BNP Level to Predict Left Ventricular Aneurysm Formation after Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Savas Celebi
Ozlem Ozcan Celebi
Serkan Cetin
Hande Ozcan Cetin
Mujgan Tek
Serkan Gokaslan
Basri Amasyali
Berkten Berkalp
Erdem Diker
Sinan Aydogdu
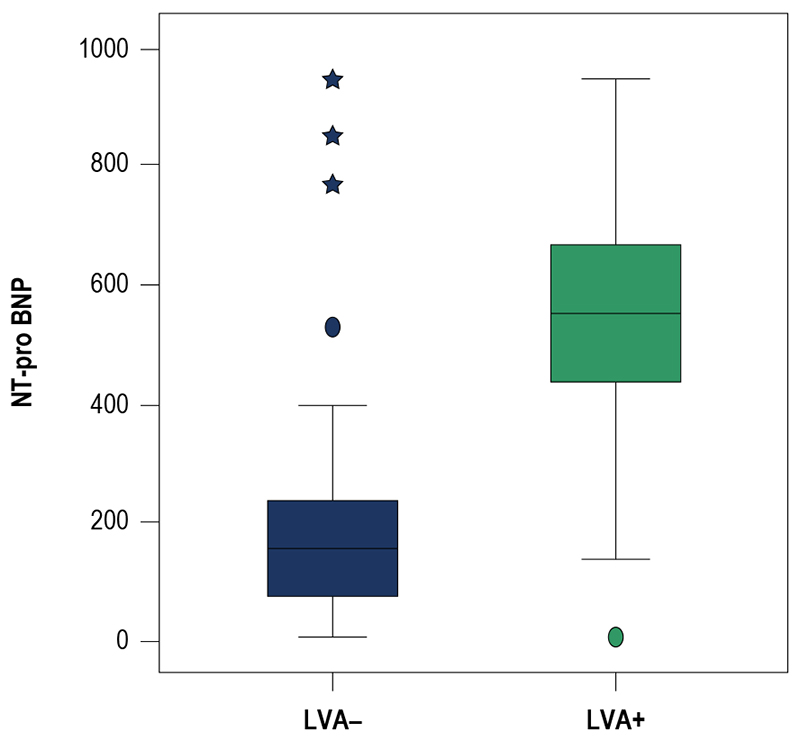
Figure 3 – Patients who developed left ventricular aneurysm after acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction had higher NT-pro BNP levels at admission. NT-pro BNP: N terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide LVA: left ventricular aneurysm.
Abstract
Background: Left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) is an important complication of acute myocardial infarction. In this study, we investigated the role of N- Terminal pro B type natriuretic peptide level to predict the LVA development after acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Methods: We prospectively enrolled 1519 consecutive patients with STEMI. Patients were divided into two groups according to LVA development within the six months after index myocardial infarction. Patients with or without LVAs were examined to determine if a significant relationship existed between the baseline N- Terminal pro B type natriuretic peptide values and clinical characteristics. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: LVA was detected in 157 patients (10.3%). The baseline N- Terminal pro- B type natriuretic peptide level was significantly higher in patients who developed LVA after acute MI (523.5 ± 231.1 pg/mL vs. 192.3 ± 176.6 pg/mL, respectively, p < 0.001). Independent predictors of LVA formation after acute myocardial infarction was age > 65 y, smoking, Killip class > 2, previous coronary artery bypass graft, post-myocardial infarction heart failure, left ventricular ejection fraction < 50%, failure of reperfusion, no-reflow phenomenon, peak troponin I and CK-MB and NT-pro BNP > 400 pg/mL at admission.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that plasma N- Terminal pro B type natriuretic peptide level at admission among other variables provides valuable predictive information regarding the development of LVA after acute STEMI. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2019; 113(6):1129-1137)
Keywords: Myocardial Infarction; Coronary Aneurysm/complications; Myocardial Revascularization; Indicators of Morbidity and Mortality; Stroke Volume.















