Volume 113, Nº 2, August 2019
DOI: http://www.dx.doi.org/10.5935/abc.20190134
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Presystolic Wave is Associated with Subclinical Left Ventricular Dysfunction Assessed by Myocardial Performance Index in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Selim Kul
İhsan Dursun
Semiha Ayhan
Muhammet Rasit Sayin
Özge Üçüncü
Nilgün Esen Bülbül
Ahmet Hakan Ateş
Ali Rıza Akyüz
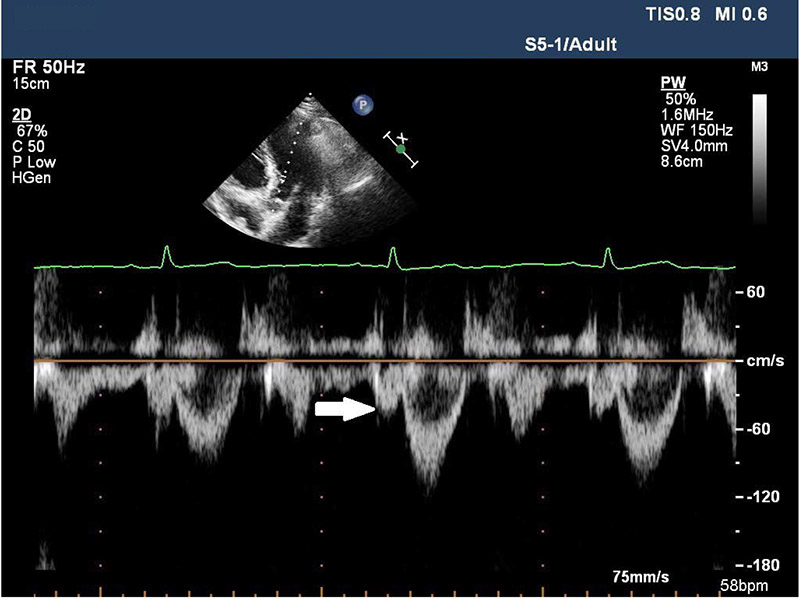
Figure 1 – Arrow shows the PSW. PSW, presystolic wave.
Abstract
Background: Myocardial performance index (MPI), demonstrates both systolic and diastolic functions of the left ventricle. Presystolic wave (PSW) is frequently detected on Doppler examination of the left ventricular outflow tract and possible mechanism of PSW is impaired LV compliance and left ventricular stiffness.
Objective: To investigate the relationship between PSW and MPI in type 2 diabetic patients.
Method: A total of 129 type 2 diabetic patients were included in this study. Patients were divided into two groups according to the presence of PSW on Doppler echocardiography. There were 90 patients (38 male, mean age 57.77 ± 10.91 years) in the PSW-positive group and 39 patients (13 male; mean age: 55.31 ± 11.29 years) in the PSW-negative group. The p values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results: MPI was higher in PSW- positive group (0.63 ± 0.17vs 0.52 ± 0.13, p < 0.001). In addition, subclinical left ventricle dysfunction (LVD) was higher in the PSW- positive group (p = 0.029). Univariate analysis showed that the presence of PSW associated with abnormal MPI (p = 0.031). Pearson correlation analysis showed that PSW velocity correlated with MPI (r: 0.286, p = 0.006).
Conclusion: Presence of the PSW on Doppler examination was associated with subclinical LV dysfunction in patients with DM type 2. This easy‑to-perform echocardiographic parameter may be related to subclinical LVD among patients with type 2 DM. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2019; 113(2):207-215)
Keywords: Heart/physiopathology; Diabetes Mellitus Type 2; Ventricular Dysfunction,Left; Heart Failure; Risk Factors.















