Volume 112, Nº 6, June 2019
DOI: http://www.dx.doi.org/10.5935/abc.20190058
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Clinical Significance of Platelet Volume and Other Platelet Parameters in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Stable Coronary Artery Disease
Liumei Ding
Lihua Sun
Feng Wang
Liejun Zhu
Ting Zhang
Fanli Hua
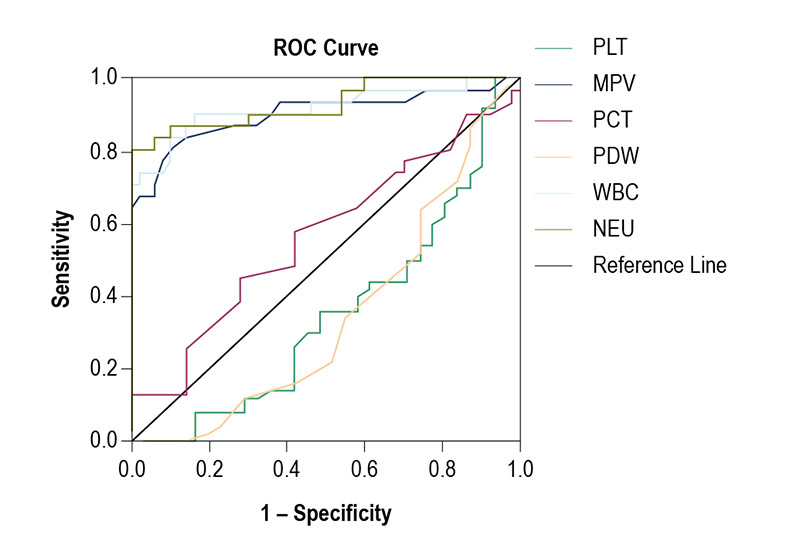
Figure 1 – ROC curves of PLT, PDW, MPV, PCT, WBC and NEU for predicting AMI. PLT: platelet count; MPV: mean platelet volume; PCT: plateletcrit; PDW: platelet distribution width; WBC: white blood cell; NEU: neutrophils; AMI: acute myocardial infarction.
Abstract
Background: Platelets are important in the initiation of thrombosis, and their morphological and functional changes are closely related with the occurrence and development of coronary artery thrombosis. Platelet parameters might be valuable in distinguishing between acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and stable coronary artery disease (SCAD).
Objective: This study was designed to detect and compare changes in platelet parameters, such as mean platelet volume (MPV) in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and stable coronary artery disease (SCAD) and to investigate their roles in these diseases. Methods: Specimen collection: Between January 2011 and December 2013, 2 mL of elbow vein blood was drawn from each of 31 patients primarily diagnosed with AMI, 34 SCAD patients and 50 healthy subjects; and placed in EDTA-K2 anticoagulant tubes. Platelet count (PLT), MPV, plateletcrit (PCT), platelet distribution width (PDW), white blood cell (WBC) and neutrophil (NEU) counts were determined using an STKS automated hematology analyzer (Beckman Courter).
Results: Compared with the control group, MPV levels were significantly higher in the AMI and SCAD groups (p < 0.05), while PLT was significantly lower (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: These results suggest that MPV and other related parameters have a certain value in the diagnosis of SCAD and AMI. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2019; 112(6):715-719)
Keywords: Acute Coronary Syndrome/physiopathology; Coronary Thrombosis; Mean Platelet Volume; Myocardial Infarction.















