Volume 112, Nº 4, April 2019
DOI: http://www.dx.doi.org/10.5935/abc.20180275
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Efficacy, Safety, and Performance of Isolated Left vs. Right Ventricular Pacing in Patients with Bradyarrhythmias: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Elizabeth Sartori Crevelari
Katia Regina da Silva
Caio Marcos de Moraes Albertini
Marcelo Luiz Campos Vieira
Martino Martinelli Filho
Roberto Costa
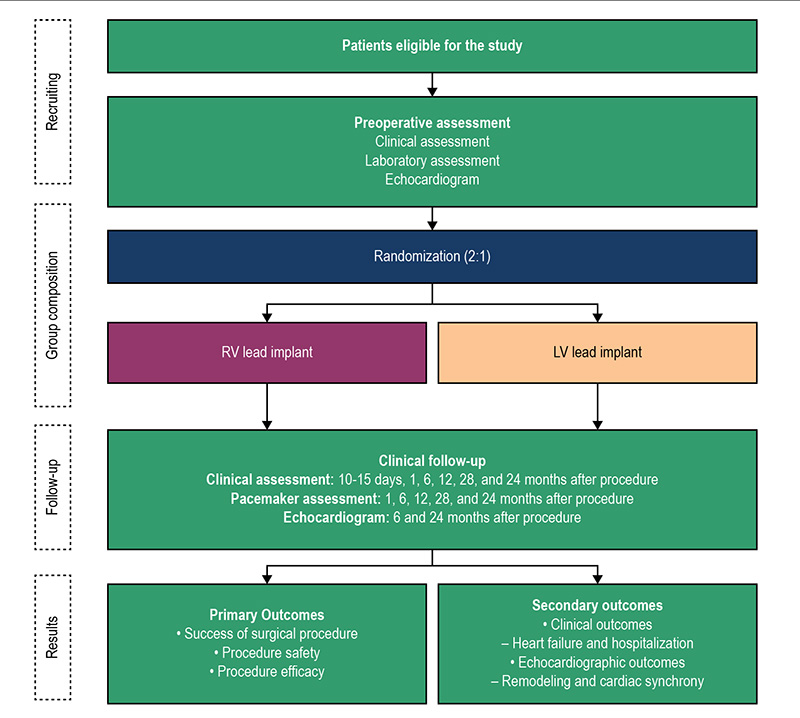
Figure 1 – Diagram showing the main phases of the study. LV: left ventricle; RV: right ventricle.
Abstract
Background: Considering the potential deleterious effects of right ventricular (RV) pacing, the hypothesis of this study is that isolated left ventricular (LV) pacing through the coronary sinus is safe and may provide better clinical and echocardiographic benefits to patients with bradyarrhythmias and normal ventricular function requiring heart rate correction alone.
Objective: To assess the safety, efficacy, and effects of LV pacing using an active-fixation coronary sinus lead in comparison with RV pacing, in patients eligible for conventional pacemaker (PM) implantation.
Methods: Randomized, controlled, and single-blinded clinical trial in adult patients submitted to PM implantation due to bradyarrhythmias and systolic ventricular function ≥ 0.40. Randomization (RV vs. LV) occurred before PM implantation. The main results of the study were procedural success, safety, and efficacy. Secondary results were clinical and echocardiographic changes. Chi-squared test, Fisher’s exact test and Student’s t-test were used, considering a significance level of 5%.
Results: From June 2012 to January 2014, 91 patients were included, 36 in the RV Group and 55 in the LV Group. Baseline characteristics of patients in both groups were similar. PM implantation was performed successfully and without any complications in all patients in the RV group. Of the 55 patients initially allocated into the LV group, active‑fixation coronary sinus lead implantation was not possible in 20 (36.4%) patients. The most frequent complication was phrenic nerve stimulation, detected in 9 (25.7%) patients in the LV group. During the follow-up period, there were no hospitalizations due to heart failure. Reductions of more than 10% in left ventricular ejection fraction were observed in 23.5% of patients in the RV group and 20.6% of those in the LV group (p = 0.767). Tissue Doppler analysis showed that 91.2% of subjects in the RV group and 68.8% of those in the LV group had interventricular dyssynchrony (p = 0.022).
Conclusion: The procedural success rate of LV implant was low, and the safety of the procedure was influenced mainly by the high rate of phrenic nerve stimulation in the postoperative period. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2019; 112(4):410-421)
Keywords: Cardiac Pacing, Artificial; Bradycardia; Arrhythmias, Cardiac; Pacemaker, Artificial; Ventricular remodeling.















