Volume 111, Nº 3, September 2018
DOI: http://www.dx.doi.org/10.5935/abc.20180152
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Fasting/Refeeding Cycles Prevent Myocardial Dysfunction and Morphology Damage in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Matheus Fécchio Pinotti
Amanda Martins Matias
Mário Mateus Sugizaki
André Ferreira do Nascimento
Maeli Dal Pai
Ana Paula Lima Leopoldo
Antônio Carlos Cicogna
André Soares Leopoldo
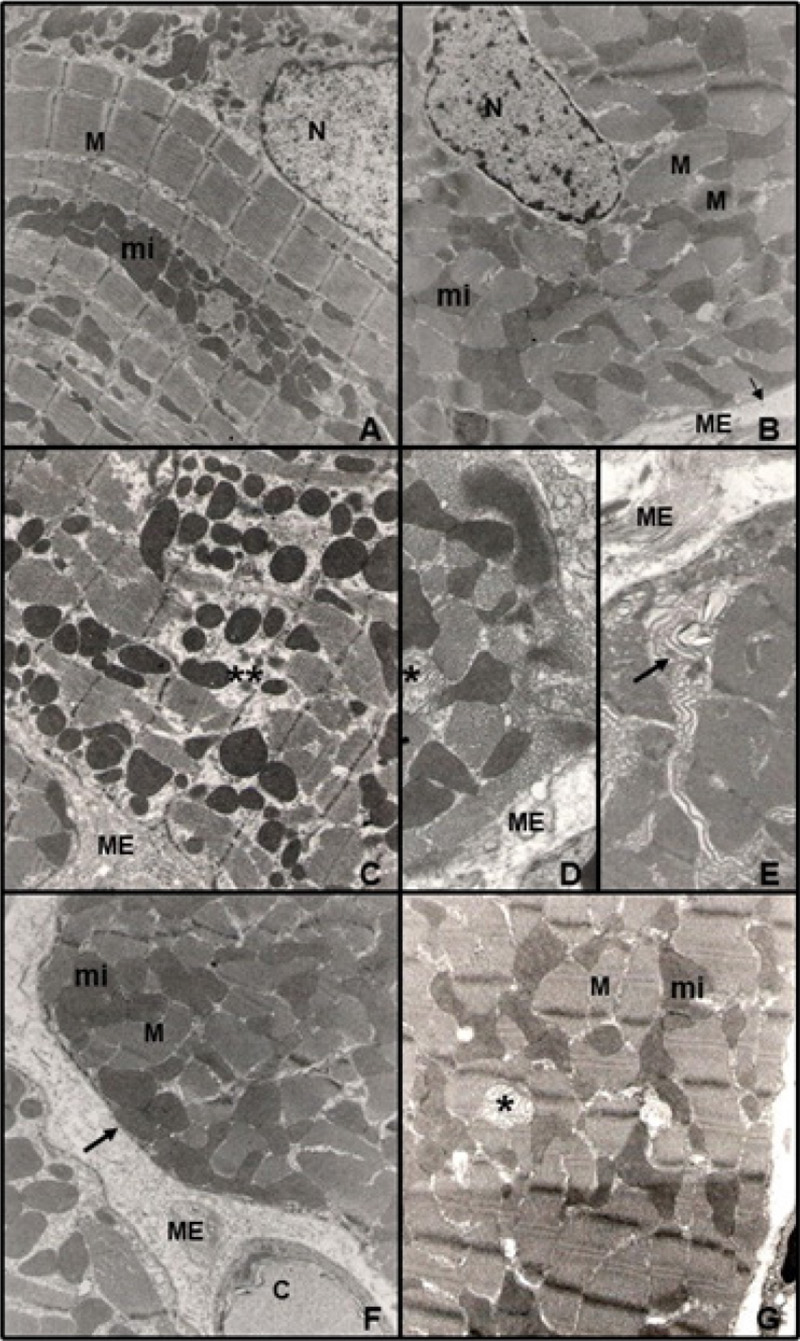
Figure 4 – Ultrastructural study of LV papillary muscle (n = 3 per group). Photographs A and B correspond to the control group, photographs C, D and E to the food restriction (R50) group and photographs F and G to the refeeding group (RF) group. The control group showed preserved ultrastructure with normal myofibrils (M), sarcoplasmic reticulum (arrowhead), mitochondria (mi), nuclear membrane (N) and plasma membrane (arrow). Food restriction rats showed cellular changes, including polymorphic mitochondria (*), myofibril disorganization (**), and infolding of the plasma membrane (arrow). The papillary muscle during refeeding showed preserved myofibrils (M), mitochondria (mi), and plasma membranes (arrow), polymorphic mitochondria (*) and capillary (C). Source: Research team.
Abstract
Background: Caloric restriction is known to impair the cardiac function and morphology in hypertrophied hearts of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR); however, the influence of fasting/refeeding (RF) is unknown.
Objective: To investigate the fasting/refeeding approach on myocardial remodeling and function. In addition, the current study was designed to bring information regarding the mechanisms underlying the participation of Ca2+ handling and β-adrenergic system.
Methods: Sixty-day-old male SHR rats were submitted to food ad libitum (C), 50% food restriction (R50) or RF cycles for 90 days. Cardiac remodeling was assessed by ultrastructure analysis and isolated papillary muscle function. The level of significance considered was 5% (α = 0.05).
Results: The RF rats presented lower cardiac atrophy than R50 in relation to C rats. The C rats increased weight gain, R50 maintained their initial body weight and RF rats increased and decreased weight during RF. The RF did not cause functional impairment because the isotonic and isometric parameters showed similar behavior to those of C. The isotonic and isometric cardiac parameters were significantly elevated in RF rats compared to R50 rats. In addition, the R50 rats had cardiac damage in relation to C for isotonic and isometric variables. While the R50 rats showed focal changes in many muscle fibers, the RF rats displayed mild alterations, such as loss or disorganization of myofibrils.
Conclusion: Fasting/refeeding promotes cardiac beneficial effects and attenuates myocardial injury caused by caloric restriction in SHR rats, contributing to reduce the cardiovascular risk profile and morphological injuries. Furthermore, RF promotes mild improvement in Ca2+ handling and β-adrenergic system. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018; 111(3):400-409)
Keywords: Rats; Hypertension; Myocardial/dysfunction; Chronic Disease; Fasting, Reffeding; Caloric Restriction.















