Volume 110, Nº 6, June 2018
DOI: http://www.dx.doi.org/10.5935/abc.20180097
REVIEW ARTICLE
Pulmonary Ultrasound in Patients with Heart Failure - Systematic Review
Rafael Tostes Muniz
Evandro Tinoco Mesquita
Celso Vale Souza Junior
Wolney de Andrade Martins
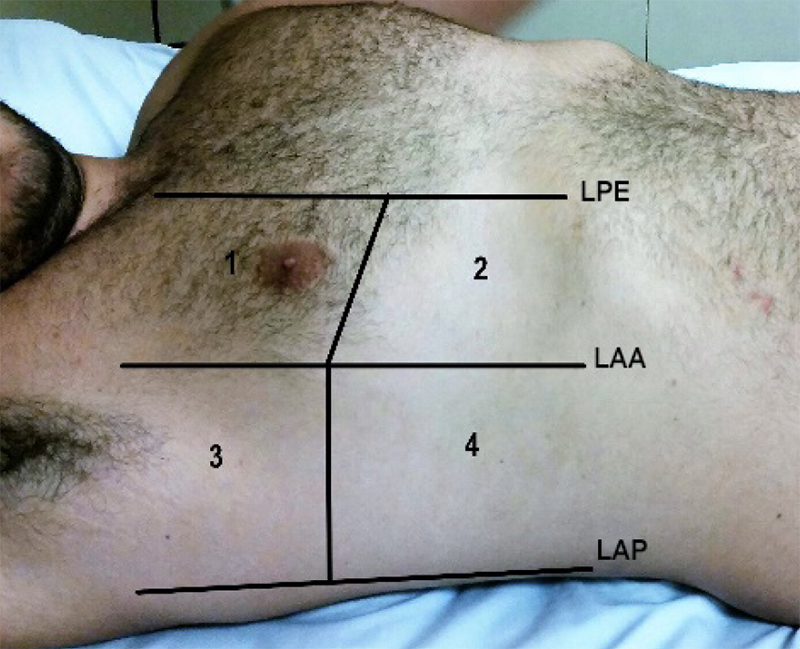
Figure 2 – Methodology for pulmonary ultrasound assessment: 8 fields (zones). Modified from Volpicelli et al.12 PSL: para-sternal line; AAL: anterior axillary line; PAL: posterior axillary line.
Abstract
Pulmonary congestion is an important clinical finding in patients with heart failure (HF). Physical examination and chest X-ray have limited accuracy in detecting congestion. Pulmonary ultrasound (PU) has been incorporated into clinical practice in the evaluation of pulmonary congestion. This paper aimed to perform a systematic review of the use of PU in patients with HF, in different scenarios. A search was performed in the MEDLINE and LILACS databases in February 2017 involving articles published between 2006 and 2016. We found 26 articles in the present review, 11 of which in the emergency setting and 7 in the outpatient setting, with diagnostic and prognosis defined value and poorly studied therapeutic value. PU increased accuracy by 90% as compared to physical examination and chest X-ray for the diagnosis of congestion, being more sensitive and precocious. The skill of the PU performer did not interfere with diagnostic accuracy. The presence of B-lines ≥ 15 correlated with high BNP values (≥ 500) and E/e' ratio ≥ 15, with prognostic impact in IC patients at hospital discharge and those followed up on an outpatient basis. In conclusion, when assessing pulmonary congestion in HF, PU has an incremental value in the diagnostic and prognostic approach in all scenarios studied.















