Volume 110, Nº 4, April 2018
DOI: http://www.dx.doi.org/10.5935/abc.20180040
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Mid-Term Results of Surgical Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation in Valvular Heart Disease Assesed by Speckle Tracking Echocardiography
Natalia Lorenzo
Irene Mendez
Mikel Taibo
Gianfranco Martinis
Sara Badia
Guillermo Reyes
Rio Aguilar
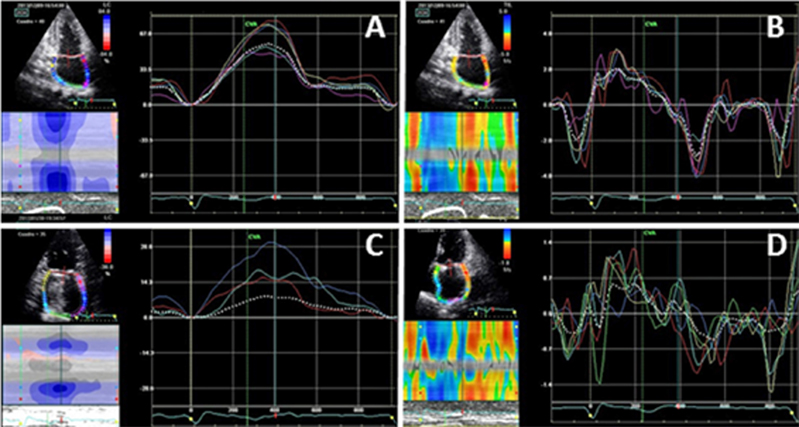
Figure 3 – Strain and strain rate curves in a healthy individual (A and B, respectively) and in a post-surgery patient (C and D, respectively).
Abstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation frequently affects patients with valvular heart disease. Ablation of atrial fibrillation during valvular surgery is an alternative for restoring sinus rhythm.
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate mid-term results of successful atrial fibrillation surgical ablation during valvular heart disease surgery, to explore left atrium post-ablation mechanics and to identify predictors of recurrence.
Methods: Fifty-three consecutive candidates were included. Eligibility criteria for ablation included persistent atrial fibrillation <10 years and left atrium diameter < 6.0 cm. Three months after surgery, echocardiogram, 24-hour Holter monitoring and electrocardiograms were performed in all candidates who maintained sinus rhythm (44 patients). Echo-study included left atrial deformation parameters (strain and strain rate), using 2-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography. Simultaneously, 30 healthy individuals (controls) were analyzed with the same protocol for left atrial performance. Significance was considered with a p value of < 0.05.
Results: After a mean follow up of 17 ± 2 months, 13 new post-operative cases of recurrent atrial fibrillation were identified. A total of 1,245 left atrial segments were analysed. Left atrium was severely dilated in the post-surgery group and, mechanical properties of left atrium did not recover after surgery when compared with normal values. Left atrial volume (≥ 64 mL/m2) was the only independent predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence (p = 0.03).
Conclusions: Left atrial volume was larger in patients with atrial fibrillation recurrence and emerges as the main predictor of recurrences, thereby improving the selection of candidates for this therapy; however, no differences were found regarding myocardial deformation parameters. Despite electrical maintenance of sinus rhythm, left atrium mechanics did not recover after atrial fibrillation ablation performed during valvular heart disease surgery. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018; 110(4):312-320)
Keywords: Ablation Techniques; Atrial Fibrillation; Heart Valve Diseases; Cryosurgery; Echocardiography.















