Volume 115, Nº 2, August 2020
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20180384
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Blood Pressure Control and Associated Factors in a Real-World Team-Based Care Center
Thiago Veiga Jardim
Ana Luiza Lima Souza
Weimar Kunz Sebba Barroso
Paulo Cesar B. Veiga Jardim
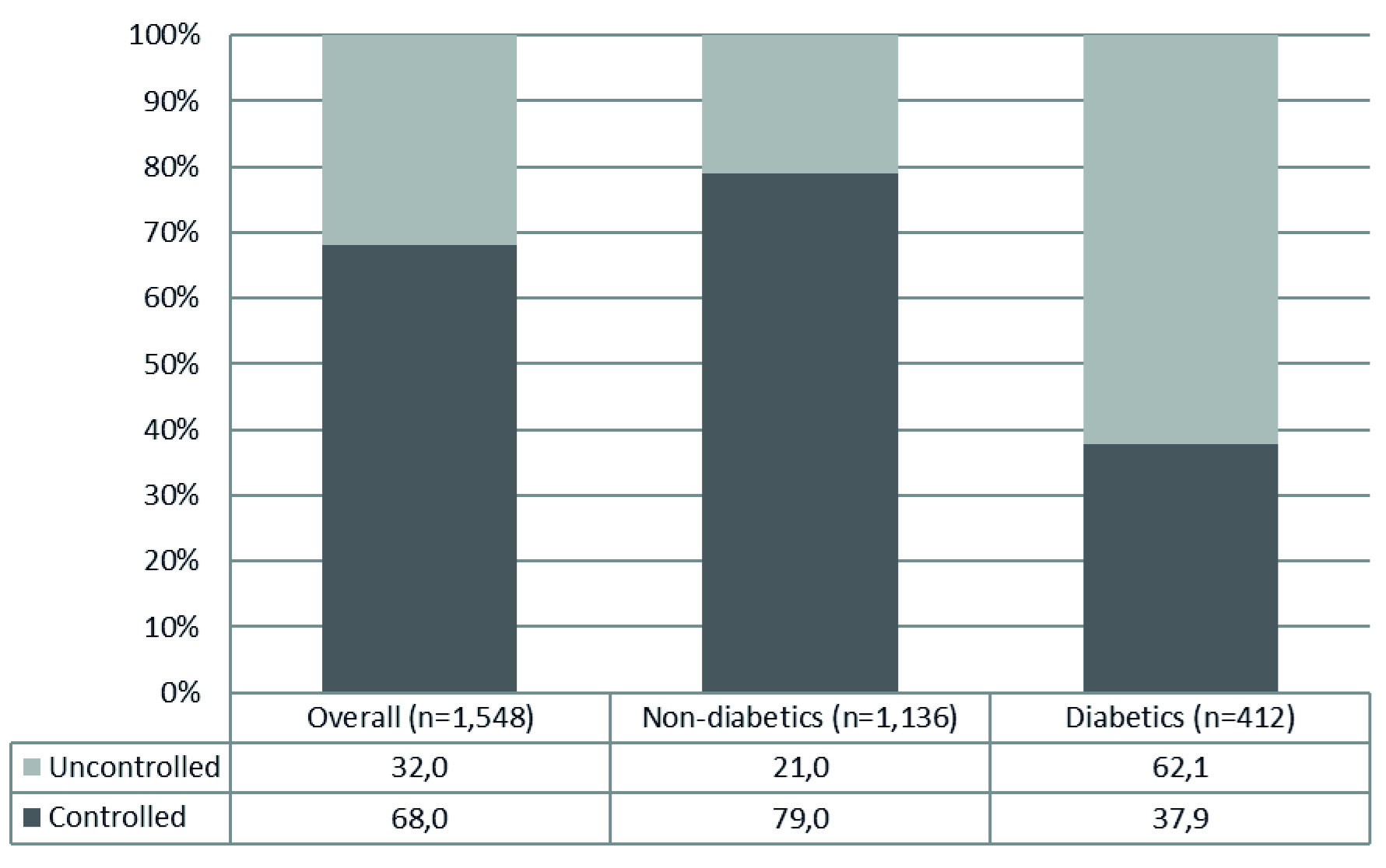
Figure 1 – Blood pressure control in the overall study population, non-diabetics and diabetics. Goiânia – Brazil. Blood pressure control – BP < 140 x 90 mmHg in nondiabetics and < 130 x 80 mmHg in diabetics.
Abstract
Background: Although team-based care is recommended for patients with hypertension, results of this intervention in a real-world setting are missing in the literature.
Objective: To report the results of a real-world long-term team-based care for hypertensive patients we conducted this study.
Methods: Data of hypertensive patients attending a multidisciplinary treatment center located in the Midwest region of Brazil in June 2017 with at least two follow-up visits were retrospectively assessed. Anthropometric, blood pressure (BP), follow-up time, pharmacological treatment, diabetes and lifestyle data were collected from the last visit to the service. BP values < 140 x 90 mmHg in non-diabetics and < 130 x 80 mmHg in diabetics were considered controlled. A logistic regression model was built to identify variables independently associated to BP control. Significance level adopted p < 0.05.
Results: A total of 1,548 patients were included, with a mean follow-up time of 7.6 ± 7.1 years. Most patients were female (73.6%; n=1,139) with a mean age of 61.8 ±12.8 years. BP control rates in all the sample, and in non-diabetics and diabetics were 68%, 79%, and 37.9%, respectively. Diabetes was inversely associated with BP control (OR 0.16; 95%CI 0.12-0.20; p<0.001) while age ≥ 60 years (OR 1.48; 95%CI 1.15-1.91; p=0.003) and female sex (OR 1.38; 95%CI 1.05-1.82; p=0.020) were directly associated.
Conclusions: A BP control rate around 70% was found in patients attending a multidisciplinary team care center for hypertension. Focus on patients with diabetes, younger than 60 years and males should be given to further improve these results. (Arq Bras Cardiol. 2020; 115(2):174-181)
Keywords: Hypertension; Blood Pressure/prevention and control; Exercise; Treatment Adherence and Compliance; Sedentarism; Obesity; Life Style.















